British warships in 1982 were armed with dozens of nuclear depth charges in a nuclear-free zone in Latin America, Richard Norton-Taylor reports.
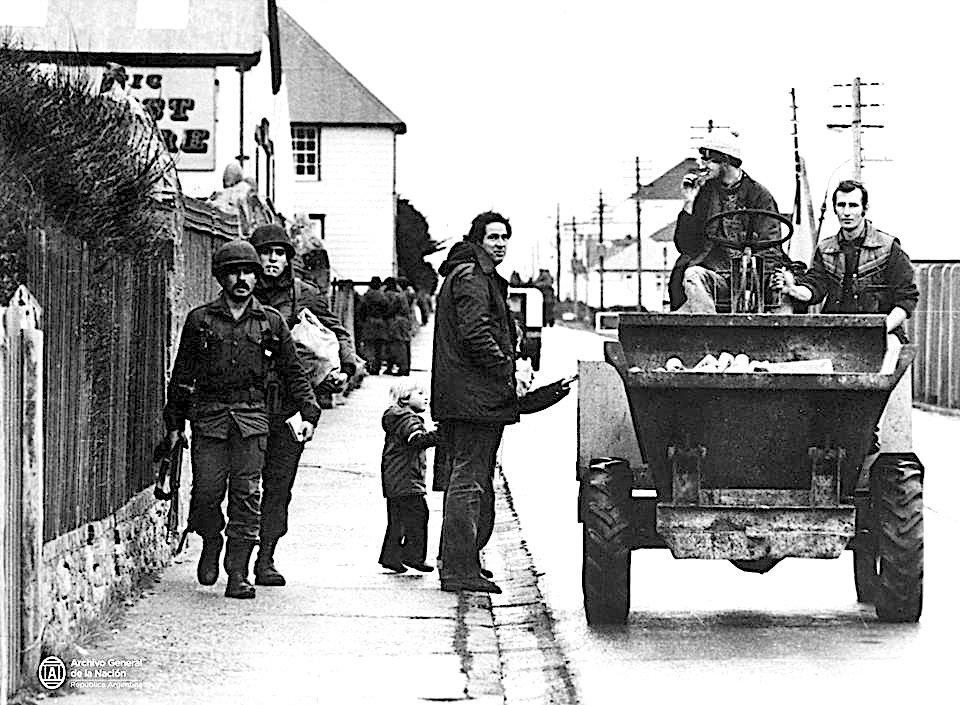

Argentinian soldiers and Falklanders in 1982. (Wikimedia Commons)
By Richard Norton-Taylor
Declassified UK
 The revelation is contained in a new file released to the National Archives. Marked “Top Secret Atomic,” it shows that the presence of the nuclear weapons caused panic among officials in London when they realized the damage, both physical and political, they could have caused.
The revelation is contained in a new file released to the National Archives. Marked “Top Secret Atomic,” it shows that the presence of the nuclear weapons caused panic among officials in London when they realized the damage, both physical and political, they could have caused.
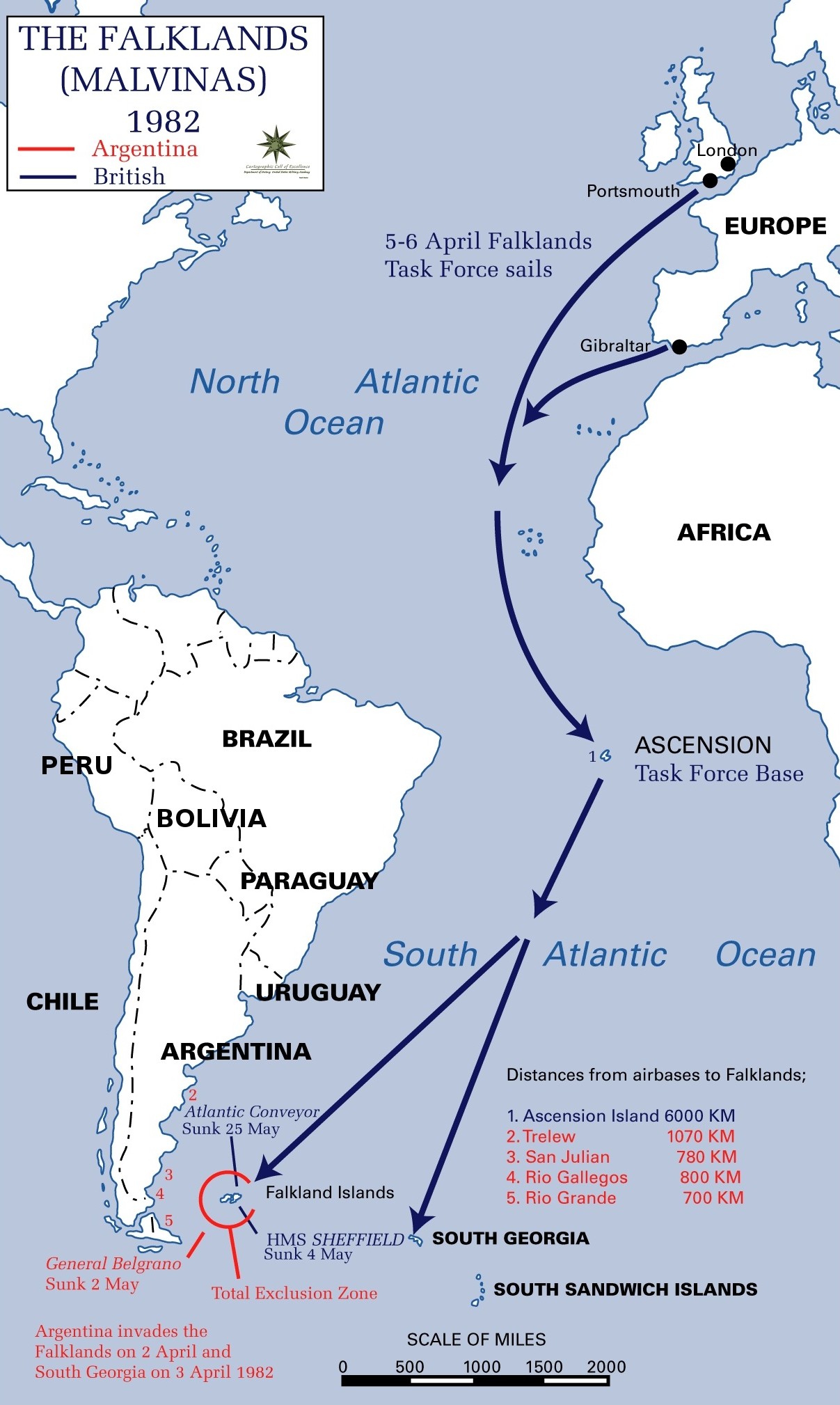
The military regime in Argentina claimed the Falkland islands and invaded on April 2, 1982. The U.K. government under Margaret Thatcher dispatched a naval task force to the South Atlantic to retake the islands.
A Ministry of Defence (MoD) minute, dated April 6, 1982, referred to “huge concern” that some of the “nuclear depth bombs” could be “lost or damaged and the fact become public.” The minute added: “The international repercussions of such an incident could be very damaging.”
Nuclear depth bombs are deployed from navy ships to attack submerged submarines.
The unidentified official who wrote the minute continued:
“The secretary of state [John Nott] will wish to continue the long-established practice of refusing to comment on the presence or absence of UK nuclear weapons at any given location at any particular time.”
Heated Row
The existence of the weapons provoked a heated row between the MoD and the Foreign Office. The latter asked the MoD to “unship” the weapons. The Navy refused to do so.
The MoD noted the principal arguments in favour of keeping the weapons on board. It stated:
“In the event of tension or hostilities between ourselves and the Soviet Union concurrent with Operation Corporate [the codename given to liberating the Falklands] the military capability of our warships would otherwise be severely reduced.”
One document in the file says there was no risk of an “atomic bomb type explosion.” But there was a threat of the “disposal of fissile material” if any of the weapons was damaged which could lead to up to 50 “additional deaths” from cancer.
Even if there was no pollution in the event of a damaged or sunk nuclear weapon the Argentinians might get hold of nuclear technology and “we might have had to face acute embarrassment in the non-proliferation field,” recorded a MoD official.
Keeping Secret
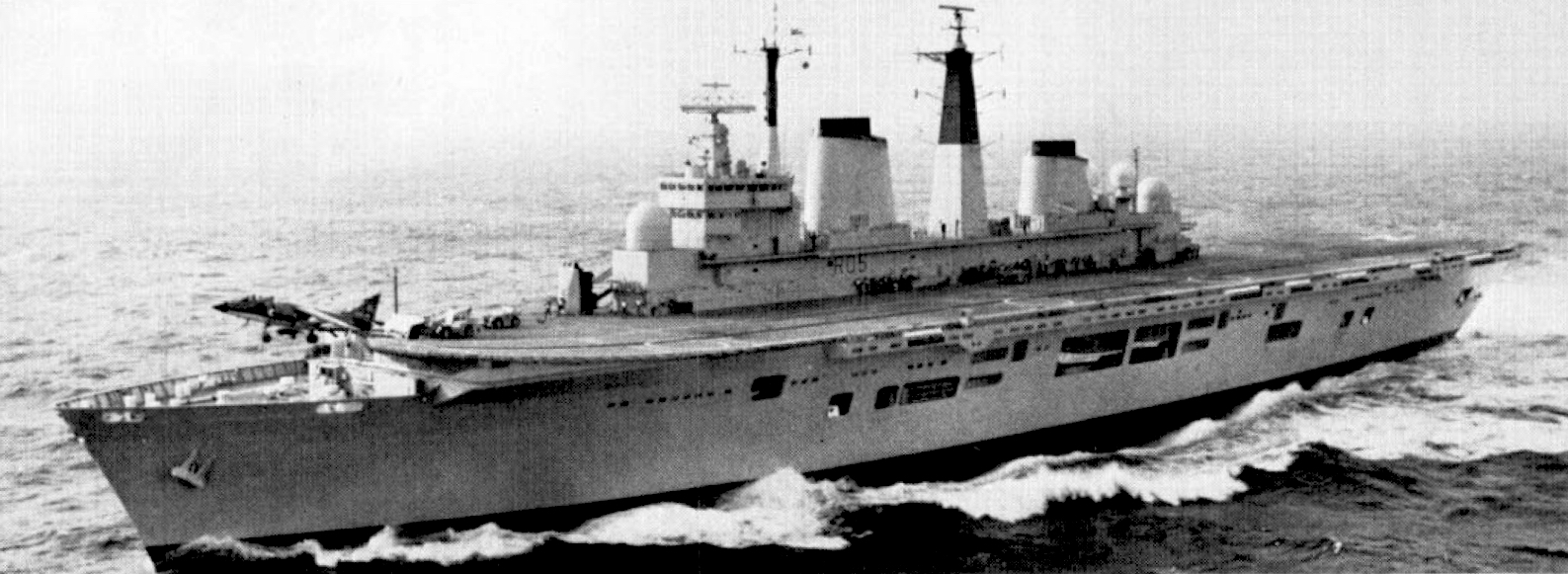

August 1981: A British Harrier jet takes off from the Royal Navy aircraft carrier HMS Invincible during fleet exercise in Norfolk, Virginia. (U.S. Navy)
A plan to offload the weapons at the British base on Ascension Island in the South Atlantic Ocean was rejected by the Navy. It said this would delay the passage of the task force to the Falklands and that the operation would not be kept secret.
Instead, the weapons were transferred from the frigates and destroyers to the larger aircraft carriers, HMS Hermes and HMS Invincible, where the weapons could be better protected. Prince Andrew served as a helicopter pilot on Invincible during the war.
By the middle of May 1982, the Hermes had 18 nuclear weapons on board and Invincible 12, while the Royal Fleet Auxiliary ship, Regent, had one, according to the file. The ships were within the “total exclusion zone” imposed by Britain around the Falkland Islands, the documents say.
The file does not say whether any of these were “inert” surveillance rounds used to monitor the “wear and tear on the weapons”, as academic Lawrence Freedman put it in his Official History of the Falklands Campaign, published in 2005.
Support CN’s Winter Fund Drive!
Surveillance and training rounds were used to test the depth charges to see how they would perform. They were identical to live weapons except the fissile material was replaced by depleted uranium and inert substances.
But even the presence of inert rounds caused alarm in the Foreign Office. Its top official, Sir Antony Ackland, wrote to Sir Frank Cooper, his opposite number in the MoD: “I was very glad to have your confirmation that HMS Sheffield was not carrying an inert round when she was hit.”
The destroyer sank on May 10, 1982 after being attacked by an Argentinian Exocet missile six days earlier.
Nuclear Free Zone
The Foreign Office was also anxious about the presence of the nuclear weapons because of the 1967 Treaty of Tlatelolco. This established a nuclear free zone in Latin America and surrounding waters, including the Falklands.
Although Britain had signed and ratified the treaty’s protocols other countries, including Argentina, had not done so. According to Freedman, Margaret Thatcher insisted that no ship carrying nuclear weapons would enter the three-mile territorial waters around the Falklands which would be a “potential breach” of the Tlatelolco treaty.
(U.S. Military Academy)
The MoD admitted in 2003 that British ships in the task force carried nuclear weapons and that a weapon container had been damaged. But the number of weapons had not been revealed before this document was transferred to the National Archives in Kew, south west London.
But a number of documents from the file have been weeded by the MoD or the Cabinet Office. They include an intriguing note, dated April 11, 1982, beginning “The Chiefs of Staff believe…” What they believed we are not allowed to know.
What About Gibraltar?
Many more documents are missing from a separate file, now declassified, entitled “Gibraltar: Impact of the Falklands Crisis”.
Gibraltarians, like the Falkland Islanders, inhabited a British “Overseas Territory” and were concerned because Spain supported Argentine claims of sovereignty over the islands just as it claimed Gibraltar, the large rock and British base on the southern tip of the Iberian peninsula.
Whitehall weeders have withheld no fewer than 73 documents from the Gibraltar file. They have done so under exemptions in the Freedom of Information Act, and, specifically, sections 27(i), 40 (2), and 41.
These cover information whose disclosure might “prejudice” the interest of the U.K. abroad, “personal data” and “information provided in confidence.” Passages in other documents in the file have also been excised.
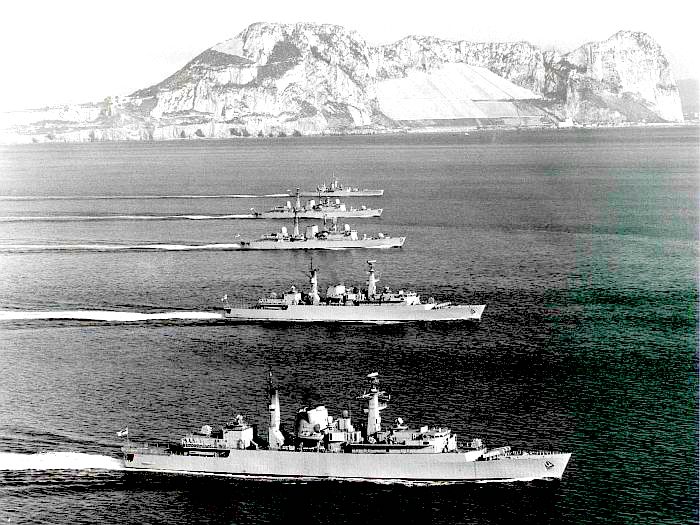

British warships, pennants painted over, off Gibraltar in March 1982, heading for the Falklands. (Pete Reeves, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons)
What has the British government to hide? Documents declassified previously may offer some clues. Thatcher repeatedly expressed concern about the implications of the Falklands crisis for Gibraltar.
Despite the public rhetoric, successive U.K. governments have been prepared to negotiate about sovereignty of the Falklands and sought a joint sovereignty agreement with Spain over Gibraltar in 2000 and again in 2002.
Thatcher’s government secretly offered to hand over sovereignty of the Falklands islands two years before the invasion by Argentine forces in 1982. The cabinet’s defence committee approved a plan whereby Britain would hand Argentina titular sovereignty over the islands, which would then be leased back by Britain for 99 years.
Lord Carrington resigned as foreign secretary over the Argentine invasion of the Falklands. He told the subsequent Franks Committee, which inquired into the run-up to the invasion, that British policy had been one of neglect and hoping for the best. “We did not have any cards in our hands”, he said.
Richard Norton-Taylor is a British editor, journalist and playwright, and the doyen of British national security reporting. He wrote for the Guardian on defence and security matters and was the newspaper’s security editor for three decades.
This article is from Declassified UK.
Support CN’s
Winter Fund Drive!
Donate securely with PayPal
Or securely by credit card or check by clicking the red button:


One quote says that the DoD did not want to remove nuclear arms to keep the ships ready for a possible conflict with USSR, would it happen while ships are in the south Atlantic. The second quote says that FO was concerned that even [ “inert” surveillance rounds used to monitor the “wear and tear on the weapons” ] were problematic, which is unclear why: as described, surveillance rounds were basically conventional depth charges, just sufficiently similar in structure to nuclear charges to be used for testing.
It is also unclear why all corvettes were equipped with such testing devices. Either FO was misinformed by DoD, or “surveillance rounds” was the description used by DoD to communicate with other ministries, and FO people knew what they really objected too.
This is the first I’ve ever even heard about nuclear depth charges. The entire concept of such a weapon is disgusting and maddening.
The stupidest jokes turn to be true. In this case, bumper stickers “Nuke the whales”.
OMG, you still can get those stickers on Amazon, for mere 3.49 USD, plus tax.
I liked it
The Yanx and the Brits…the asses of evil – like two peas in the same pod. But their ‘sun’ is setting…
” . . . their ‘sun’ is setting…” which means Our Sun is setting too.